Scaling Autonomous Vulnerability Triage: Closing the Data-to-Context Gap in Agentic Security Systems
By Varun Nikhil G. Chopra
Abstract
As security findings grow in volume and complexity, manual triage becomes the dominant bottleneck in incident response and detection engineering. Large language models offer promising capabilities for automated reasoning but in practice are constrained by data noise, limited context windows, and uncontrolled operational cost.
This paper presents an architecture designed for production environments that automates vulnerability triage by combining stateful agentic reasoning using LangGraph and OpenAI GPT-4o with high signal data retrieval from AWS DynamoDB. By applying filtering at the attribute level within the data layer, implementing recursive pagination to overcome DynamoDB scan limits, and enforcing cost governance through automated IAM circuit breakers, the system enables reliable and scalable research workflows. The result is an autonomous research agent capable of prioritizing high impact vulnerabilities while remaining observable, deterministic, and financially bounded.
1. Problem Statement
Security researchers increasingly face a signal-to-noise crisis. Public vulnerability sources such as NVD and CISA KEV expose massive JSON payloads that were designed for human consumption and archival completeness, not automated reasoning.
Naively passing this data to an LLM introduces several failure modes:
- Token Latency: Irrelevant metadata increases prompt size, slowing the reasoning loop and reducing throughput.
- Context Dilution: Critical details are frequently lost in long prompts, a phenomenon commonly described as "lost in the middle."
- Operational Risk: Autonomous reasoning loops without governance can generate unbounded API usage and cloud spend.
Effective autonomous triage requires treating data selection, context construction, and cost control as first-class engineering problems rather than prompt-tuning exercises.
2. The Reasoning Engine: Model Selection
For the agent's core reasoning engine, I selected OpenAI GPT-4o. In an agentic workflow, the model's ability to consistently generate valid JSON for tool calling is more critical than raw creative output. GPT-4o was chosen for three specific architectural advantages:
- Reliable Function Calling: The model demonstrates low hallucination rates when translating natural language research queries into structured DynamoDB scan parameters.
- Reasoning Latency: The low latency of GPT-4o allows the LangGraph state machine to complete multi-step reasoning loops in seconds rather than minutes.
- Contextual Awareness: The model effectively maintains a memory of previous scan results to avoid redundant database calls during extended research sessions.
Implementation Highlight: LLM Initialization
I utilized the ChatOpenAI class from the LangChain community package, configuring the temperature to 0 to ensure deterministic, reproducible security analysis. Additionally, I enabled streaming to surface the agent's internal reasoning tokens in real time, providing critical observability and reducing the time to first insight during long running research tasks.
Python
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0,
streaming=True
)
3. Architectural Pillars
Stateful Reasoning with LangGraph
LangGraph was selected over linear agent chains to support explicit state management, branching, and backtracking. This allows the agent to verify intermediate conclusions and re-query data when confidence is insufficient, a requirement for security-sensitive research.
High-Signal Data Retrieval
DynamoDB Projection Expressions were used to remove non-essential fields at the storage layer. By retrieving only product identifiers, severity indicators, and CVE metadata, payload size was reduced by approximately 60 percent before reaching the LLM.
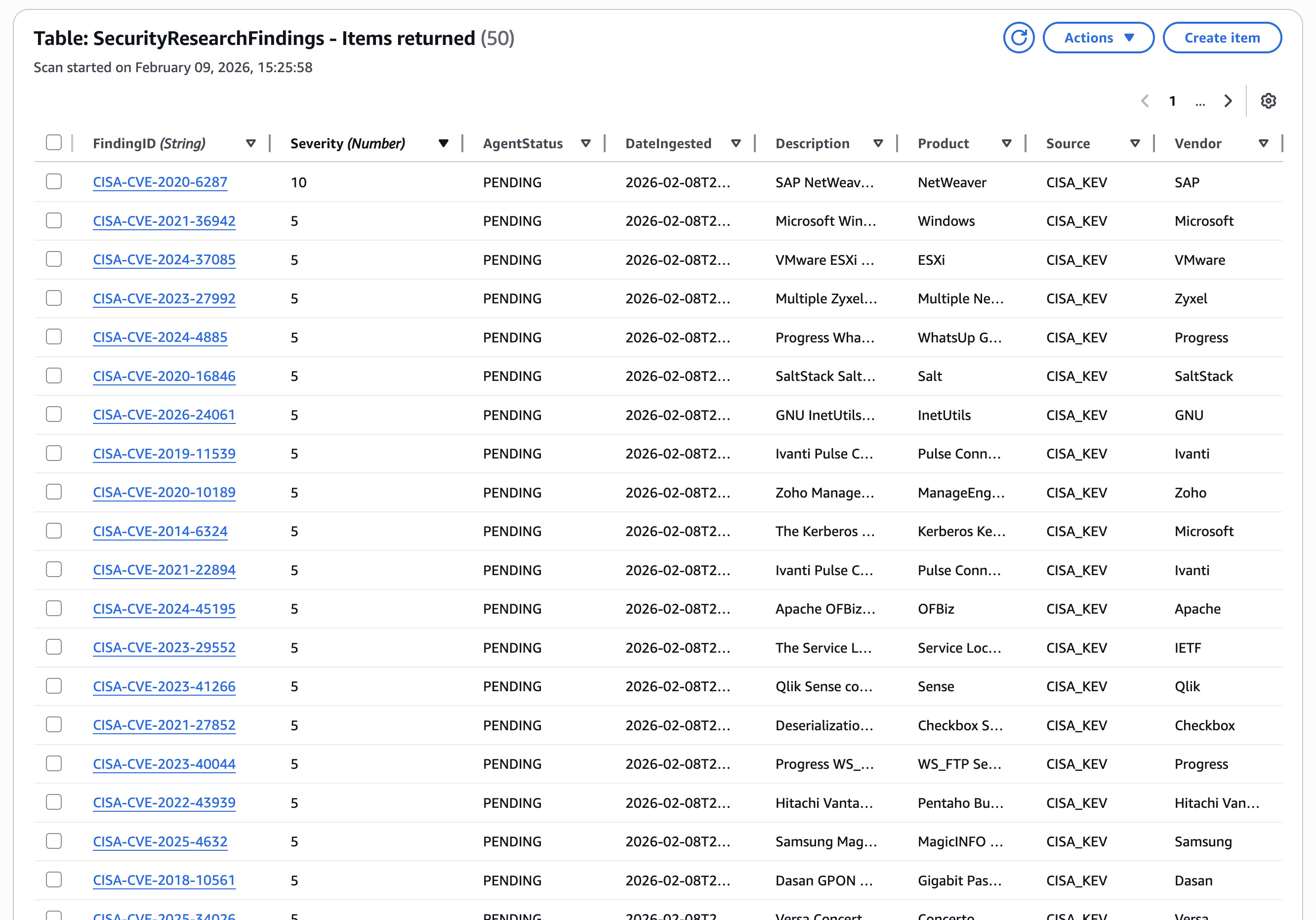
Overcoming the DynamoDB 1MB Scan Limit
DynamoDB's native scan limit introduces blind spots when applied to security datasets. A recursive pagination strategy was implemented to ensure complete ingestion of high-severity findings, guaranteeing comprehensive coverage.
Governance as Code
Autonomous systems require enforceable guardrails. AWS Budget Actions were used to apply automated IAM policy revocation if a fixed daily budget threshold was exceeded, creating a hard circuit breaker that physically prevents runaway execution.
4. Implementation Details
The system is implemented as a modular, tool-augmented architecture. Rather than relying on a monolithic prompt, data retrieval, state management, and cost governance are intentionally separated into independent layers.
A. Recursive Pagination for Complete Dataset Coverage
DynamoDB scan operations are limited to 1MB per request, which can exclude critical records in large
partitions. The system detects the LastEvaluatedKey and recursively continues scanning until
the dataset is fully traversed, ensuring no high-severity vulnerabilities are missed.
B. Context Window Optimization through Attribute Filtering
The primary challenge in autonomous triage is the signal to noise ratio. Security databases often contain extensive metadata that is useful for storage but irrelevant for high level reasoning. To address this, I implemented attribute filtering using projection expressions. By explicitly selecting only high signal attributes such as product name, severity, vulnerability identifiers, and risk summaries, I successfully stripped out approximately sixty percent of the nonessential noise from each record.
This optimization serves a critical architectural purpose by mitigating the lost in the middle phenomenon documented in recent language model research. Studies have demonstrated that model performance often follows a curve where accuracy degrades when critical information is buried in the middle of a long context window. By aggressively pruning the data at the retrieval layer, I ensured that the most relevant security findings remain within the high attention primacy and recency zones of the model. This strategic reduction of the input volume prevents hallucination and ensures that the agent reasoning remains grounded in the most impactful data points.
C. Enforced Cost Governance
AWS Budget Actions monitor spend in near real time. When the defined threshold is reached, an automated
Lambda applies an AWSDenyAll policy to the agent's IAM role, immediately severing access and
preventing further execution. This mechanism provides deterministic cost containment without relying on
application-level safeguards.
5. Reasoning Trace Visualization
A Streamlit-based dashboard was developed to expose the agent's internal reasoning steps, tool invocations, and decision boundaries. By making the reasoning trace observable, the system enables rapid human validation and iterative improvement without relying on opaque LLM outputs.
Figure 1: Streamlit dashboard interface showing the initial agent state and query input
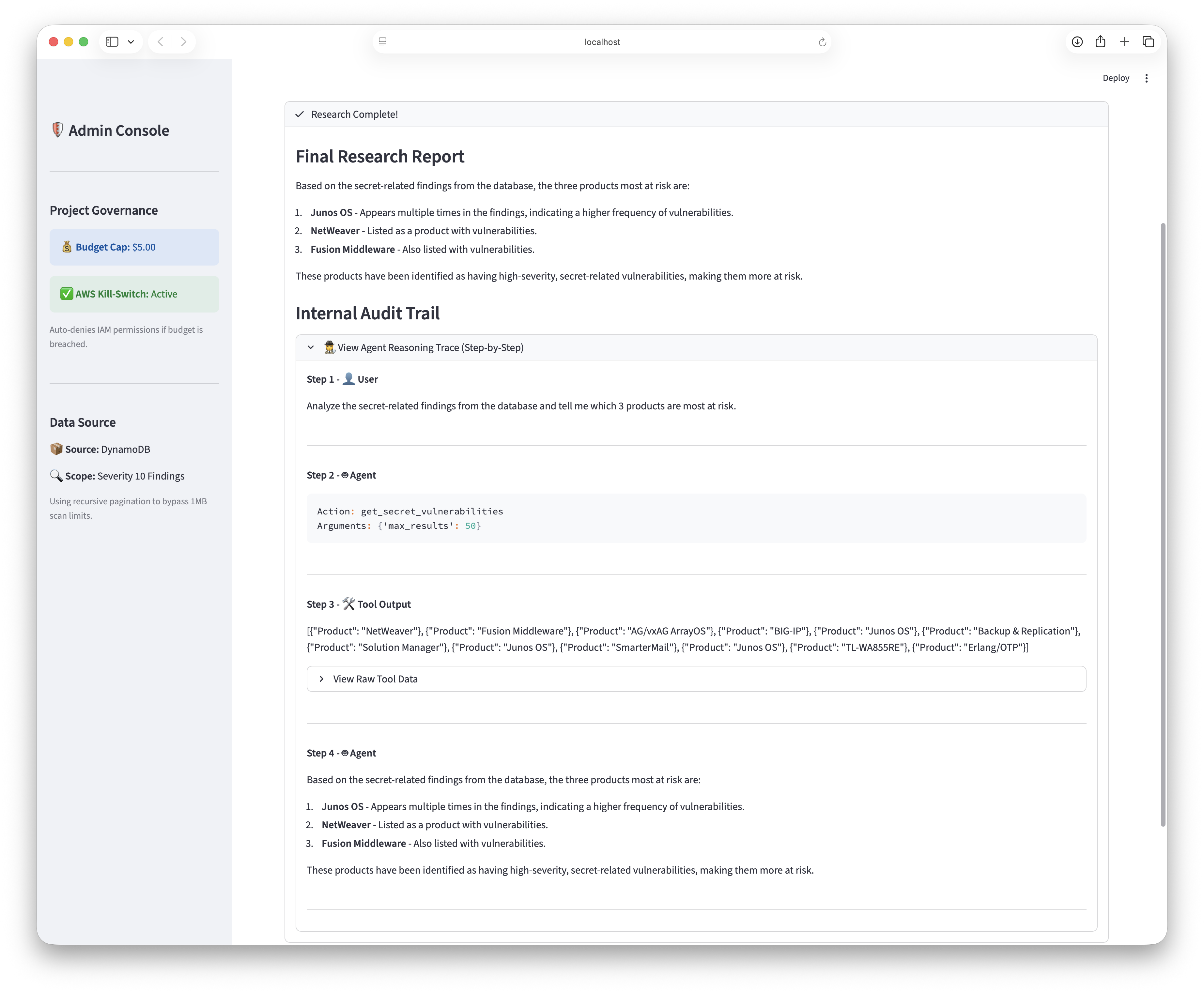
Figure 2: Complete reasoning trace showing tool invocations, decision boundaries, and final vulnerability analysis
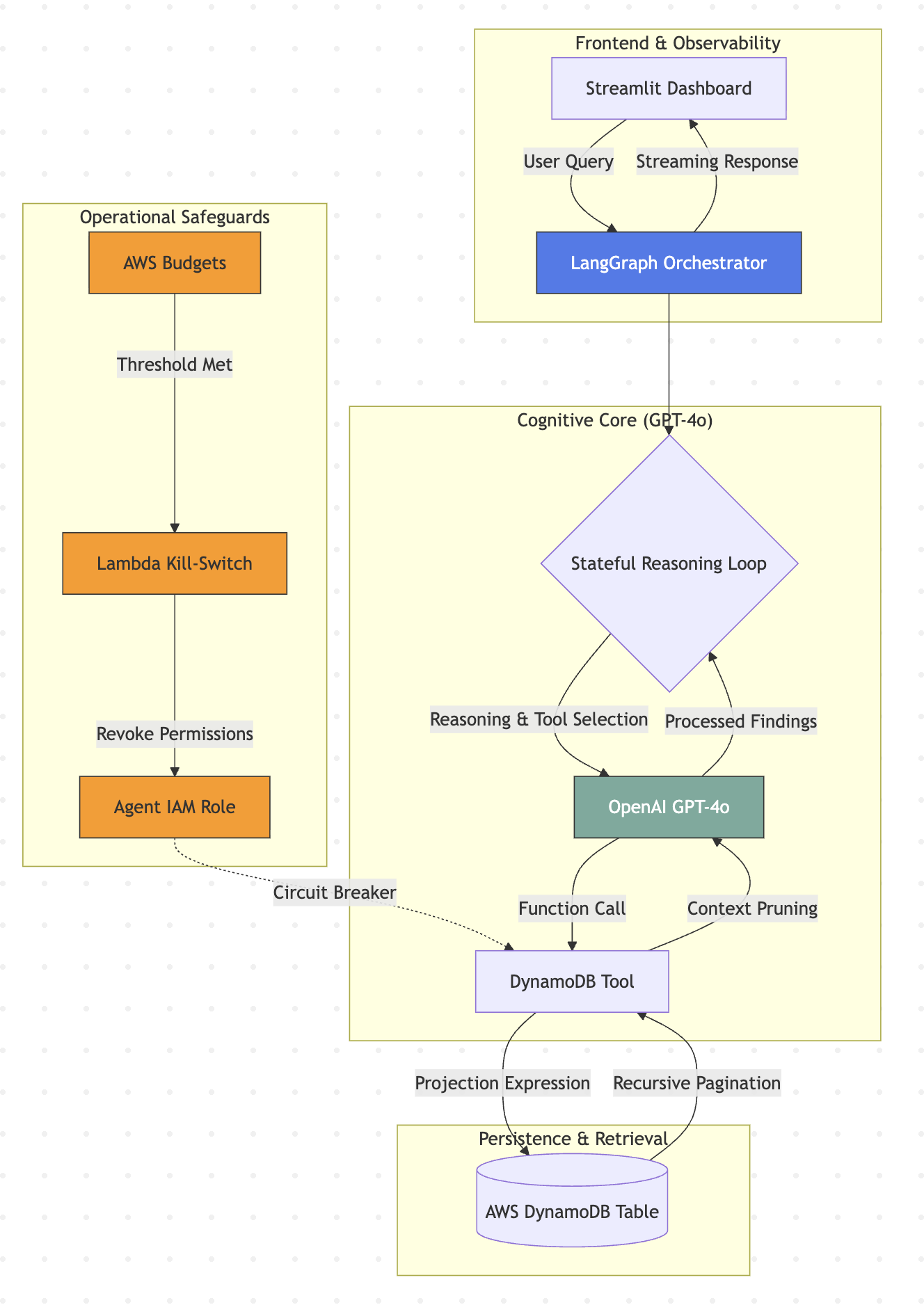
6. System Architecture
The following diagram illustrates the system architecture, showing the interaction between the user interface, agentic core, and governance layer:
📘 Deep Dive Available
For a comprehensive breakdown of the AWS infrastructure, IAM policies, and cloud architecture patterns, view the detailed technical implementation guide.
View AWS Architecture Guide →7. Conclusion
This architecture demonstrates that autonomous security agents must do more than generate text. By treating the LLM as an orchestrator, the database as a high-signal tool, and governance as enforceable infrastructure, the system enables scalable, observable, and financially bounded vulnerability research.
The result is an agent that does not merely chat about findings, but actively performs research in a way that is compatible with production security environments.
8. References
-
CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
https://www.cisa.gov/known-exploited-vulnerabilities-catalog -
LangGraph Documentation
LangChain AI
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/ -
National Vulnerability Database
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
https://nvd.nist.gov/ -
Amazon DynamoDB Developer Guide
Amazon Web Services
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/ -
Streamlit Documentation
Streamlit Inc.
https://docs.streamlit.io -
AWS Budgets - Configuring Budget Actions
Amazon Web Services
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cost-management/latest/userguide/budgets-controls.html -
Boto3 Documentation - AWS SDK for Python
Amazon Web Services
https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/index.html -
Lost in the Middle: How Language Models Use Long Contexts
Liu, N. F., Lin, K., Hewitt, J., Paranjape, A., Bevilacqua, M., Petroni, F., & Liang, P. (2024)
Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Volume 12
https://aclanthology.org/2024.tacl-1.9/